The Australian dollar slipped lower as concerns over China’s deflation risks dampened market sentiment, weighing on currencies tied to global growth. The ongoing weakness in China’s economy, Australia’s largest trading partner, has raised fears of slower demand, putting further pressure on the Aussie dollar.
China’s latest inflation data showed persistent deflationary pressures, signaling weak domestic demand and sluggish recovery momentum. This has fueled speculation that Beijing may need to implement additional stimulus measures, but doubts remain over their effectiveness in driving sustained economic growth. With Australia’s economy heavily reliant on Chinese trade, any signs of prolonged weakness in China tend to weigh on the AUD.
Meanwhile, a stronger U.S. dollar has added to the Australian dollar’s struggles. Rising U.S. bond yields and expectations that the Federal Reserve will maintain higher interest rates for longer have kept demand for the greenback elevated, limiting the Aussie’s ability to recover. Investors remain cautious as risk appetite falters, further pressuring commodity-linked currencies like the AUD.
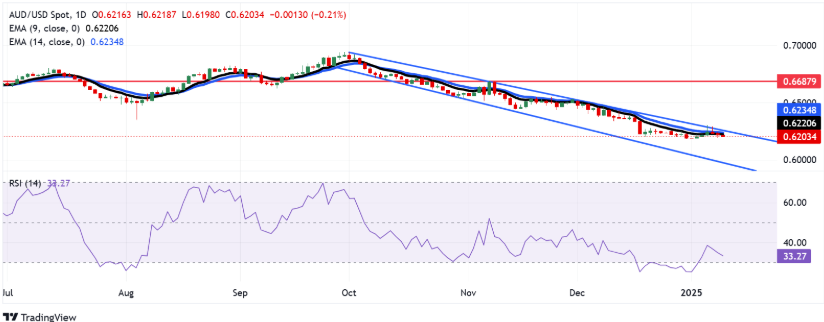
AUD/USD 1-D Chart as of January 9th, 2025 (Source: TradingView)
Domestically, the Reserve Bank of Australia’s monetary stance has also played a role. While inflation remains a concern, recent economic indicators suggest that the RBA may hold rates steady, reducing the appeal of the AUD relative to currencies backed by more aggressive central banks. Traders are watching for further guidance from policymakers, but for now, the currency remains under pressure.
With global uncertainty persisting and China’s economic struggles unresolved, the Australian dollar’s outlook remains fragile. Any further deterioration in China’s data or a prolonged rally in the U.S. dollar could push the AUD lower, leaving investors focused on upcoming economic releases for further direction.